What is an Actuator Valve and How Does It Work?
Actuator valves play a crucial role in various industrial processes. These devices control the flow of fluids by adjusting the valve opening. According to a recent market research report, the actuator valve market is expected to reach $8 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 6%. This growth is driven by the demand for automation in industries, enhancing efficiency and safety.
In many industries, actuator valves ensure precision in fluid management. They are commonly found in oil and gas, chemical production, and water treatment systems. Improperly functioning actuator valves can lead to inefficiencies and costly downtime. Many facilities struggle with outdated systems, which raises safety concerns. Additionally, organizations must reflect on the need for regular maintenance to prevent such failures.
The technology behind actuator valves is advancing rapidly. Innovations include smart actuators with feedback systems. These developments promise improved reliability and control. However, organizations must consider the investment in new technology carefully. Balancing cost and efficiency remains a challenge in many sectors today.

What is an Actuator Valve? A Comprehensive Overview
An actuator valve is a vital component in many fluid control systems. It enables automatic regulation of fluid flow in pipes. Typically, these valves operate using mechanical, electrical, or pneumatic inputs. The actuator transforms these inputs into precise movements. This allows for quick adjustments to the valve's opening or closing positions.
Understanding how actuator valves function is crucial for optimizing system efficiency. Many designs include feedback mechanisms. These help ensure that the valve remains in the desired position. However, not all actuator valves perform flawlessly. Some may face wear and tear over time, leading to performance issues. Regular maintenance becomes essential to avoid costly downtimes.
In many applications, actuator valves can be complex. They often require proper calibration to function correctly. A miscalibrated valve can result in inefficient flow regulation. This directly affects the overall system performance. Hence, familiarity with the operational principles of these valves is essential for engineers and operators alike.
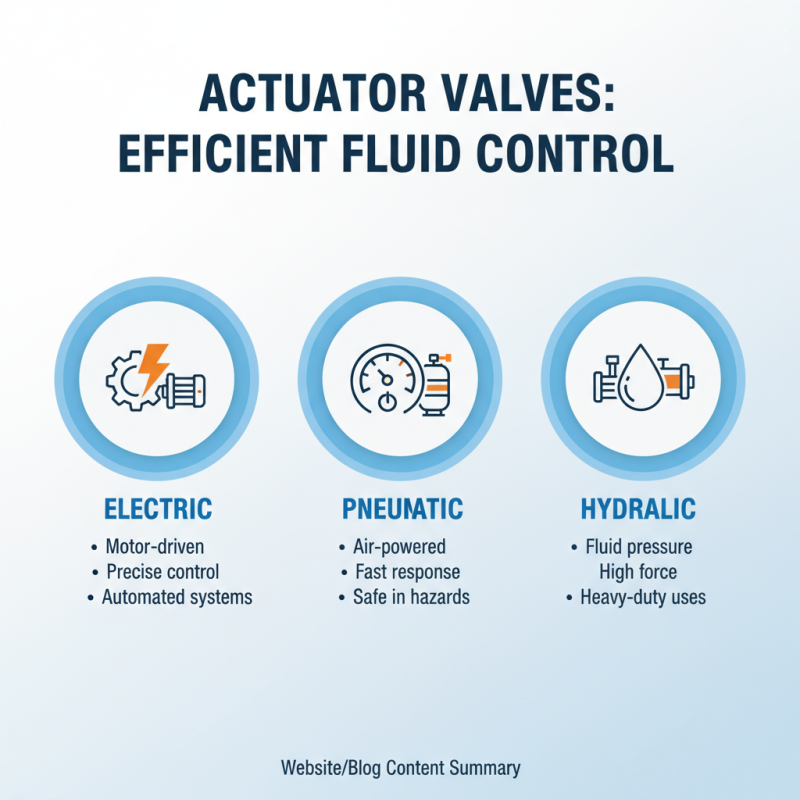
Types of Actuator Valves: Electric, Pneumatic, and Hydraulic
Actuator valves are crucial components in various systems. They help control fluid flow efficiently. There are three main types of actuator valves: electric, pneumatic, and hydraulic. Each type has unique features and applications.
Electric actuator valves utilize electric motors to operate. They can be precise and easy to control. However, they may struggle in very high-pressure environments. Pneumatic actuator valves rely on compressed air. They respond quickly to changes, making them suitable for many industrial applications. One downside is their dependence on a continuous air supply, which can be a limiting factor.
Hydraulic actuator valves use pressurized fluids for movement. These valves can generate significant force, making them ideal for heavy-duty tasks. Yet, they require careful maintenance. Leaks can be a serious issue, causing loss of fluid and power. Each type has its own strengths and weaknesses, making the choice dependent on specific needs and conditions.
Mechanism of Action: How Actuator Valves Operate
Actuator valves are essential components in various systems. They regulate the flow of liquids or gases. The mechanism of action is quite fascinating. An actuator valve uses a motor or pneumatic system to move a spindle or gate, controlling the flow path. This simple yet effective movement has numerous applications in industries.
The actuator receives signals from control systems. These signals dictate its position, either fully open, closed, or partially open. It’s remarkable how these valves can respond in real-time to changes. The technology often relies on sensors and feedback loops. However, the interaction between components can sometimes be complex. Troubleshooting issues may require careful investigation.
Sometimes, the system may not respond as expected. Malfunctions can occur due to mechanical wear or misalignment. Regular maintenance is crucial for optimal performance. Despite their reliability, actuator valves have limitations. Understanding these nuances can improve functionality and efficiency in operations. The design is not foolproof; engineering adjustments might be necessary.
Actuator Valve Performance Data
This chart illustrates the operational efficiency of different types of actuator valves based on their response time and pressure handling capabilities.
Applications of Actuator Valves in Various Industries
Actuator valves play a crucial role in various industries. These devices control the flow of liquids and gases in systems. According to a recent market report, the global actuator valve market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.2% from 2023 to 2030. This growth reflects their increasing adoption in sectors like oil and gas, water treatment, and food processing.
In the oil and gas industry, actuator valves ensure safe and efficient operations. They help regulate pressure and flow in pipelines, minimizing the risk of spills. In wastewater treatment plants, these valves manage water flow, contributing to environmental sustainability. However, installation issues and maintenance challenges can arise. Regular checks are crucial to ensure optimal performance.
The food processing sector also benefits from actuator valves. They ensure the precise flow of ingredients, maintaining quality and safety. Efficient operation contributes to reduced waste and increased productivity. Yet, the complexity of these systems can lead to unexpected failures. Identifying potential points of failure is essential for reliability.
What is an Actuator Valve and How Does It Work? - Applications of Actuator Valves in Various Industries
| Industry |
Application |
Type of Actuator Valve |
Functionality |
| Oil and Gas |
Flow Control |
Electric Actuator Valve |
Automated flow regulation and safety cut-off |
| Water Treatment |
Chemical Addition |
Pneumatic Actuator Valve |
Precise control of chemicals in treatment processes |
| Food and Beverage |
Ingredient Mixing |
Hydraulic Actuator Valve |
Ensures consistent ingredient proportions |
| HVAC |
Temperature Control |
Electric Actuator Valve |
Regulates air flow for efficient heating/cooling |
| Pharmaceuticals |
Process Automation |
Electric Actuator Valve |
Maintains sterile conditions and precise dosages |
Key Performance Metrics and Standards for Actuator Valves
Actuator valves play a vital role in various industries, enabling precise control over fluid flow. Their performance is often assessed using key metrics. These include response time, operating pressure, and position accuracy. A quick response time can enhance system efficiency. However, inconsistent performance can lead to unreliable operations.
Standards for actuator valves help establish benchmarks. These standards ensure compatibility across different systems and applications. Performance metrics like durability and maintenance needs are also critical. A valve may function well initially but could suffer from wear over time. Regular assessments are necessary to mitigate unexpected failures.
In practice, actuator valves must meet specific environmental conditions. Temperature changes, for example, can affect their operation. Monitoring these conditions helps maintain optimal performance. Each application has unique challenges. Learning from performance data can foster improvements. It's essential to remain adaptable in implementation.
 © Copyright 2020 Tianjin Tanghaidongyang Valve Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
© Copyright 2020 Tianjin Tanghaidongyang Valve Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.